Colchicine Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Colchicine
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (kol' chi seen)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Colchicine is used to prevent gout attacks (sudden, severe pain in one or more joints caused by abnormally high levels of a substance called uric acid in the blood) in adults, and to relieve the pain of gout attacks when they occur. Colchicine is also used to treat familial Mediterranean fever (FMF; an inborn condition that causes episodes of fever, pain, and swelling of the stomach area, lungs, and joints) in adults and children 4 years of age and older. Colchicine is not a pain reliever and cannot be used to treat pain that is not caused by gout or FMF. Colchicine is in a class of medications called anti-gout agents. It works by stopping the natural processes that cause swelling and other symptoms of gout and FMF.
How should this medicine be used?
Colchicine comes as a tablet to take by mouth with or without food. When colchicine is used to prevent gout attacks or to treat FMF, it is usually taken once or twice a day. When colchicine is used to relieve the pain of a gout attack, one dose is usually taken at the first sign of pain and a second, smaller dose is usually taken one hour later. If you do not experience relief or have another attack within several days after treatment, talk to your doctor before taking additional doses of medication. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take colchicine exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
If you are taking colchicine to treat FMF, your doctor may start you on a low dose and gradually increase your dose. Your doctor may decrease your dose if you experience side effects.
If you are taking colchicine to prevent gout attacks, call your doctor right away if you experience a gout attack during your treatment. Your doctor may tell you to take an extra dose of colchicine, followed by a smaller dose one hour later. If you take extra doses of colchicine to treat a gout attack, you should not take your next scheduled dose of colchicine until at least 12 hours have passed since you took the extra doses.
Colchicine can prevent attacks of gout and control FMF only as long as you take the medication. Continue to take colchicine even if you feel well. Do not stop taking colchicine without talking to your doctor.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking colchicine,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to colchicine, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in colchicine tablets. Ask your doctor or pharmacist or check the medication guide for a list of ingredients.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional products, and herbal supplements you are taking, have taken within the past 14 days, or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: antibiotics such as azithromycin (Zithromax), clarithromycin (Biaxin), and erythromycin (E.E.S., E-Mycin), telithromycin (Ketek), antifungals such as fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Sporanox), and ketoconazole (Nizoral); aprepitant (Emend); cholesterol-lowering medications (statins) such as atorvastatin (Lipitor), fluvastatin (Lescol), lovastatin (Mevacor), pravastatin (Pravachol), and simvastatin (Zocor); cyclosporine (GenGraf, Neoral, Sandimmune); digoxin (Digitek, Lanoxin); diltiazem (Cardizem, Dilacor, Tiazac, others); fibrates such as bezafibrate, fenofibrate (Antara, Lipofen), and gemfibrozil (Lopid); medications for HIV or AIDS such as amprenavir (Agenerase), atazanavir (Reyataz), fosamprenavir (Lexiva), indinavir (Crixivan), nelfinavir (Viracept), ritonavir (in Kaletra, Norvir), and saquinavir (Invirase); nefazodone; ranolazine (Ranexa); and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin, Verelan). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had kidneyor liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking colchicine, call your doctor.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Colchicine may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of the following symptoms are severe or do not go away :- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- stomach cramps or pain
- muscle pain or weakness
- numbness in the fingers or toes
- unusual bruising or bleeding
- sore throat, fever, chills, and other signs of infection
- weakness or tiredness
- paleness or grayness of the lips, tongue, or palms
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Gout Suppressants
- Tubulin Modulators
- Musculo-Skeletal System
- Preparations With No Effect on Uric Acid Metabolism
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2B6 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2B6 Inhibitors
- CYP2B6 Inhibitors (strong)
- CYP2E1 Inhibitors
- CYP2E1 Inducer
| Prescribed | For treatment and relief of pain in attacks of acute gouty arthritis. |
| Weight : | 399.437 |
| Structure | Colchicine |
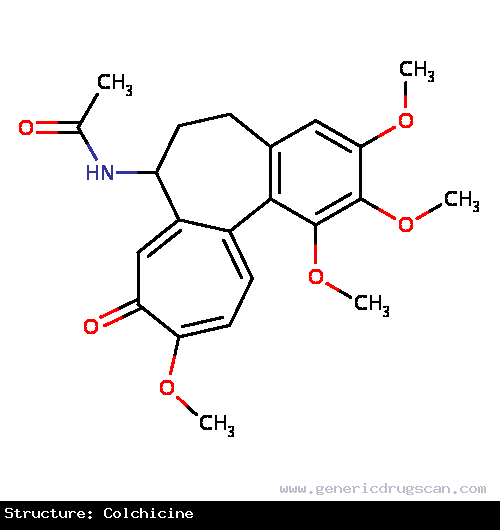 | |
| Formula | C22H25NO6 |
Colchicine has 5 Brands listed
| Colchicindon (0.5 mg) | Coljoy (0.5 mg) |
| Gountnil (0.5 mg) | Goutnil (0.5 mg) |
| Zycolchin (0.5 mg) |
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
