Clarithromycin Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Clarithromycin
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (kla rith' roe mye sin)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Clarithromycin is used to treat certain bacterial infections, such as pneumonia (a lung infection), bronchitis (infection of the tubes leading to the lungs), and infections of the ears, sinuses, skin, and throat. It also is used to treat and prevent disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection
- a type of lung infection that often affects people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Antibiotics such as clarithromycin will not work for colds, flu, or other viral infections. Taking antibiotics when they are not needed increases your risk of getting an infection later that resists antibiotic treatment.
How should this medicine be used?
Clarithromycin comes as a tablet, an extended-release (long-acting) tablet, and a suspension (liquid) to take by mouth. The regular tablet and liquid are usually taken with or without food every 12 hours (twice a day) for 7 to 14 days. The long-acting tablet is usually taken with food every 24 hours (once a day) for 7 to 14 days. Your doctor may tell you to take clarithromycin for a longer time depending on your condition. Take clarithromycin at around the same time(s) every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take clarithromycin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Shake the suspension well before each use to mix the medication evenly.
The tablets should be taken with a full glass of water. Swallow the long-acting tablets whole; do not split, chew, or crush them.
You should begin to feel better during the first few days of treatment with clarithromycin. If your symptoms do not improve or get worse, call your doctor.
Take clarithromycin until you finish the prescription, even if you feel better. If you stop taking clarithromycin too soon, or skip doses, your infection may not be completely treated and the bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking clarithromycin,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to clarithromycin, azithromycin (Zithromax, Zmax), dirithromycin (Dynabac) (not available in the U.S.), erythromycin (E.E.S., E-Mycin, Erythrocin), telithromycin (Ketek), any other medications, or any of the ingredients in clarithromycin tablets or suspension. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor if you are taking astemizole (Hismanal) (not available in the U.S.),cisapride (Propulsid), colchicine (Colcrys), dihydroergotamine (DHE 45, Migranal), ergotamine (Ergomar, in Cafergot, in Migergot), lovastatin (Mevacor, in Advicor) pimozide (Orap), simvastatin (Zocor, in Vytorin), or terfenadine (Seldane) (not available in the U.S.). Your doctor will probably tell you not to take clarithromycin if you are taking one or more of these medications.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had prolonged QT interval (a rare heart problem that may cause fainting or irregular heartbeat) or ventricular arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythms) or if you have ever had jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) or other liver problems while taking clarithromycin, Your doctor will probably tell you not to take clarithromycin.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what other prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: anticoagulants ('blood thinners') such as warfarin (Coumadin); certain benzodiazepines such as alprazolam (Xanax), midazolam (Versed), and triazolam (Halcion); bromocriptine (Parlodel); calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine (Norvasc, in Caduet, in Lotrel), diltiazem (Cardizem, Dilacor, Tiazac), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin, Verelan, in Tarka); carbamazepine (Tegretol); certain medications for HIV such as atazanavir (Reyataz), didanosine (Videx), efavirenz (Sustiva, in Atripla), nevirapine (Viramune), nelfinavir (Viracept), ritonavir (Norvir, in Kaletra), saquinavir (Invirase), and zidovudine (AZT, Retrovir); certain medications for irregular heartbeat such as amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone), disopyramide (Norpace), dofetilide (Tikosyn), procainamide (Procanbid), quinidine, and sotalol (Betapace); cholesterol-lowering medications (statins) such as atorvastatin (Lipitor, in Caduet) and pravastatin (Pravachol); cilostazol (Pletal); cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune); darifenacin (Enablex); digoxin (Digitek, Lanoxin); erlotinib (Tarceva); eszopiclone (Lunesta); fluconazole (Diflucan); insulin; itraconazole (Sporanox); methylprednisolone (Medrol); omeprazole (Prilosec); oral medications for diabetes such as nateglinide (Starlix), pioglitazone (Actos, in Actoplus Met, in Duetact), repaglinide (Prandin, in Prandimet), and rosiglitazone (Avandia, in Avandamet, in Avandaryl); phenytoin (Dilantin); ranitidine (Zantac); rifabutin (Mycobutin); rifampin (Rifadin, Rifamate, rifampicin, Rimactane); rifapentine (Priftin); sildenafil (Viagra); tacrolimus (Prograf); theophylline (Theo-Dur); tadalafil (Cialis, Adcirca); tolterodine (Detrol); valproate (Depacon); valproic acid (Depakote); vardenafil (Levitra); and vinblastine. Many other medications may also interact with clarithromycin, so tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking, even those that do not appear on this list. Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have a low level of magnesium or potassium in your blood, or if you have or have ever had an irregular heartbeat, or kidney, or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking clarithromycin, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking clarithromycin.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Clarithromycin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach pain
- heartburn
- gas
- change in taste
- headache
- rash
- hives
- itching
- swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, eyes, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- hoarseness
- peeling or blistering skin
- fever
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- extreme tiredness
- unusual bleeding or bruising
- lack of energy
- loss of appetite
- pain in the upper right part of the stomach
- dark-colored urine
- flu-like symptoms
- fast, pounding, or irregular heartbeat
- muscle weakness such as difficulty chewing, talking, or performing daily activities
- double vision
Clarithromycin may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store the tablets at room temperature and away from light, excess heat, and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Do not refrigerate the suspension. Keep it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture. Throw away any unused suspension after 14 days. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Anti-Bacterial Agents
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
- Macrolides
- Alimentary Tract and Metabolism
- Antibacterials for Systemic Use
- Antiinfectives for Systemic Use
- Macrolides, Lincosamides and Streptogramins
- Drugs for Peptic Ulcer and Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease (Gord)
- Drugs for Acid Related Disorders
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inducers
- Cytochr
| Prescribed | An alternative medication for the treatment of acute otitis media caused by H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, or S. pneumoniae in patients with... |
| Weight : | 747.9534 |
| Structure | Clarithromycin |
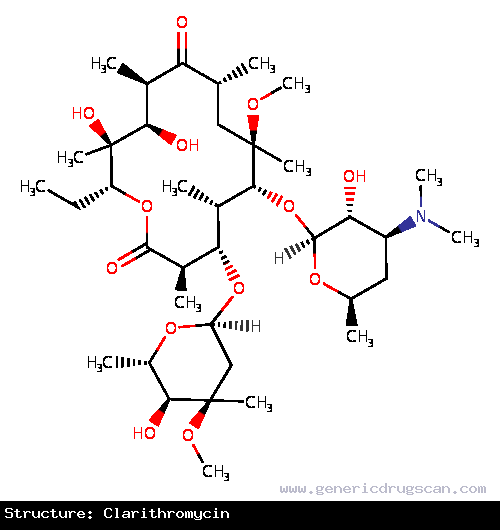 | |
| Formula | C38H69NO13 |
Clarithromycin has 141 Brands listed
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
